Bio-lab - Biology lab report
Notre Dame Catholic Sixth Form College - LeedsLeeds
Academic year: 2022/2023
Uploaded by :
Anonymous Student
This document has been uploaded by a student, just like you, who decided to remain anonymous.
Recommended for you

Core 1 - Investigate the membrane structure including the effect of alcohol concentration and temperature on membrane permeability
biology a level

AQA A level biology Practicals AND Questions
biology a level
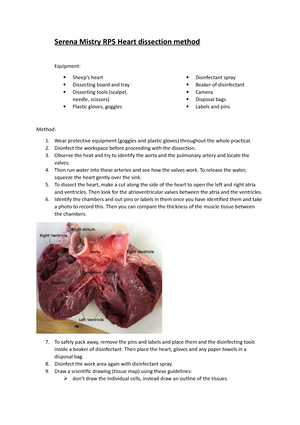
RP 5- heart dissection method
biology a level
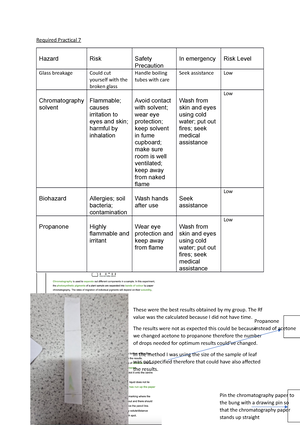
Biology rp7
biology a level
Assignments
Bio-molecules - practice questions for biological molecules aqa a level
biology a level
Practice materials
Comments
Please sign in or register to post comments.
Students also viewed
Related documents
Preview text
Figure 1: The production of yeast
Title: The effect of temperature on the rate of respiration in yeast.
AN INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECT OF
TEMPERATURE ON RESPIRATION IN YEAST
Aim: To investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of respiration in yeast with the use
of a redox indicator.
Variables
Dependent – The time, measured in seconds, taken for the mixture to turn colourless
Independent – Temperature, measured in degree Celsius.
Control variables:
2cm 3 of the yeast and glucose mixture
2cm 3 methylene blue
Introduction
Yeasts, known scientifically as saccharomyces cerevisiae, are unicellular fungi and needs
energy for its living and growth which gets from respiration. Yeast is crucial in wine-making,
baking and brewing.
Yeast respires because it forms a reaction with glucose; enzymes inside the yeast’s cells
catalyse this reaction. This is because of the successful collisions between the substrates and
the enzyme when heated up. The optimum temperature for enzymes in this reaction is 35 –
40. Below this temperature they work less efficiently and above this temperature the
enzymes denature as there is more kinetic energy which breaks the bonds leading to the
active site changing shape. Therefore, enzyme-substrate complexes will not be formed. [2]
Figure 2: Temperature affecting the enzyme activity.






